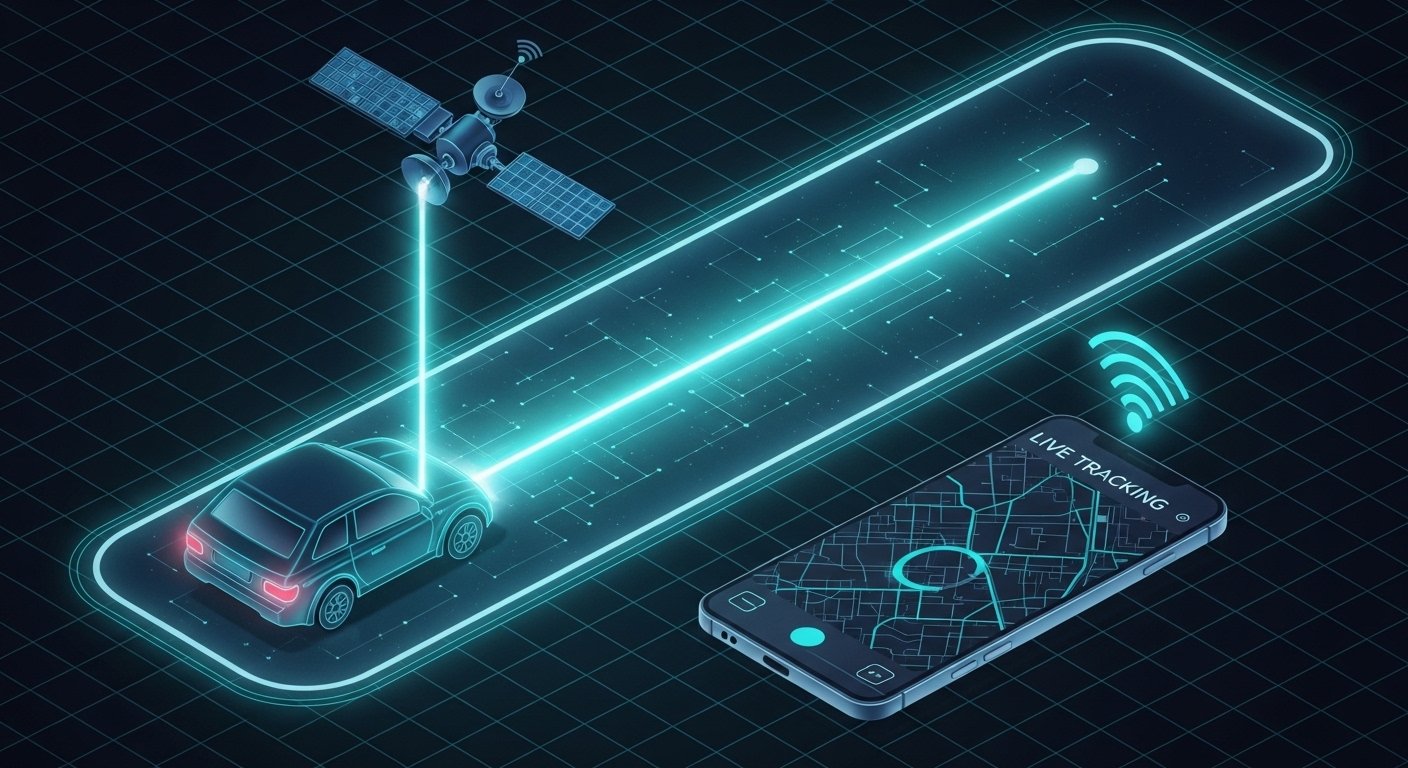
Sistema de colocação global (GPS) A tecnologia mudou essencialmente a maneira como navegamos e nos comunicamos com o mundo sobre nós. Inicialmente desenvolvido para fins militares durante toda a batalha fria, Desde então, a tecnologia GPS penetrou em vários aspectos da vida cotidiana, Da navegação individual para o gerenciamento de logística complexa. Em seu núcleo, A tecnologia GPS depende de uma rede de satélites que orbitam o planeta, que transmitir indica que permite um receptor GPS determinar seu local exato através de um procedimento conhecido como triangulação de satélite. Isso envolve medir o intervalo entre o receptor e pelo menos 4 satélites para identificar sua posição precisa.
O desenvolvimento da tecnologia GPS foi incrível. Dispositivos GPS muito precoces, que eram volumosos e limitados em funcionalidade, proporcionaram caminho para pequenos, Sistemas altamente avançados que alimentam tudo, desde telefones celulares até o sistema GPS Surack365 usado no Advanced Car Fleet Management. Atualmente, os sistemas de proteção de veículos modernos geralmente incorporam recursos de GPS avançados. Esta progressão foi de propriedade de melhorias consideráveis na tecnologia de satélite, indicar fórmulas de processamento, e nível de sensibilidade receptor, que melhoraram em conjunto a precisão e a confiabilidade das informações do GPS.
Sistemas GPS modernos, como o rastreador GPS Protrack, Ofereça precisão incomparável, frequentemente dentro de alguns metros, e pode fornecer informações sobre o local em tempo real. Esses sistemas desempenham um papel crucial na prevenção de roubos de veículos e são um elemento -chave do sistema de alarmes modernos do Sistema de Alarmes Imobilizadores Tecnologias. Apesar desses desenvolvimentos, A tecnologia GPS tem suas restrições, especialmente em atmosferas onde o satélite indica que pode ser obstruído, como desfiladeiros metropolitanos ou bosques grossos. Além disso, Fatores como problemas atmosféricos e indicam multipath podem apresentar erros. No entanto, desenvolvimentos em andamento, consistindo na integração de várias outras constelações de satélite e métodos avançados de correção de erro, prossiga para reduzir esses desafios, GPS de produção Um dispositivo essencial em indústrias variando de aplicativos individuais de navegação para GPS para negócios, e melhorar a eficácia de soluções de sistema de roubo de solução duráveis.
À medida que a tecnologia de direção autônoma passa a criar, O papel dos sistemas GPS está acabando sendo progressivamente crítico. Fornecendo informações precisas e confiáveis do local, Sistemas como o sistema GPS Surack365 são essenciais para navegar, planejamento de caminhos, e garantir a segurança e a eficácia dos veículos autônomos. A interação entre a tecnologia GPS e a direção autônomo representa um avanço considerável no transporte, prometendo maior benefício, melhor gerenciamento de tráfego, e melhorou a segurança ao dirigir, enquanto também reforça os recursos de imobilizador de alarme de carro avançado.
GPS em veículos autônomos: Como funciona
No mundo da direção autônoma, A integração da tecnologia GPS é crítica. Ao contrário dos veículos tradicionais, Veículos autônomos dependem muito de uma rede avançada de unidades e sistemas de detecção para navegar e fazer escolhas em tempo real. O sistema GPS Surack365, para circunstâncias, é uma base nesta complexa Internet de tecnologias, fornecendo informações essenciais para o planejamento de caminhos, Navegando em tempo real, e colocando precisão. Esses sistemas avançados de proteção de veículos são cruciais para a integridade funcional.
No centro do sistema de navegação de um veículo autônomo, existe o receptor GPS, que interage com os satélites para determinar o local preciso do veículo. Esta informação é depois daquela fundida com informações de várias outras unidades de detecção, como Lidar, radar, e cames de vídeo. LIDAR (Descoberta leve e variável) usa pulsos a laser para produzir mapas 3D detalhados dos ambientes do veículo, Enquanto o radar vê objetos e mede sua velocidade e alcance. Cames de vídeo fornecem informações estéticas, auxiliando para determinar as indicações da estrada, marcações de pista, e desafios.
O Suracy GPS Tracker funciona como um elemento importante neste sistema incorporado, garantir que o veículo preserve a colocação precisa nas perpetuidades. Para veículos autônomos, A precisão é fundamental; também pequenas discrepâncias podem levar a consideráveis erros de navegação. É aqui que os sistemas GPS de alta precisão, como cinemática em tempo real (RTC) e colocação precisa de pontos (PPP), entre em jogo. Esses sistemas avançados melhoram a precisão do GPS para o grau de centímetro, o que é crucial para empregos como manutenção da pista e evasão de desafio, e fortalecer as funções imobilizadoras do sistema de alarme de carro.
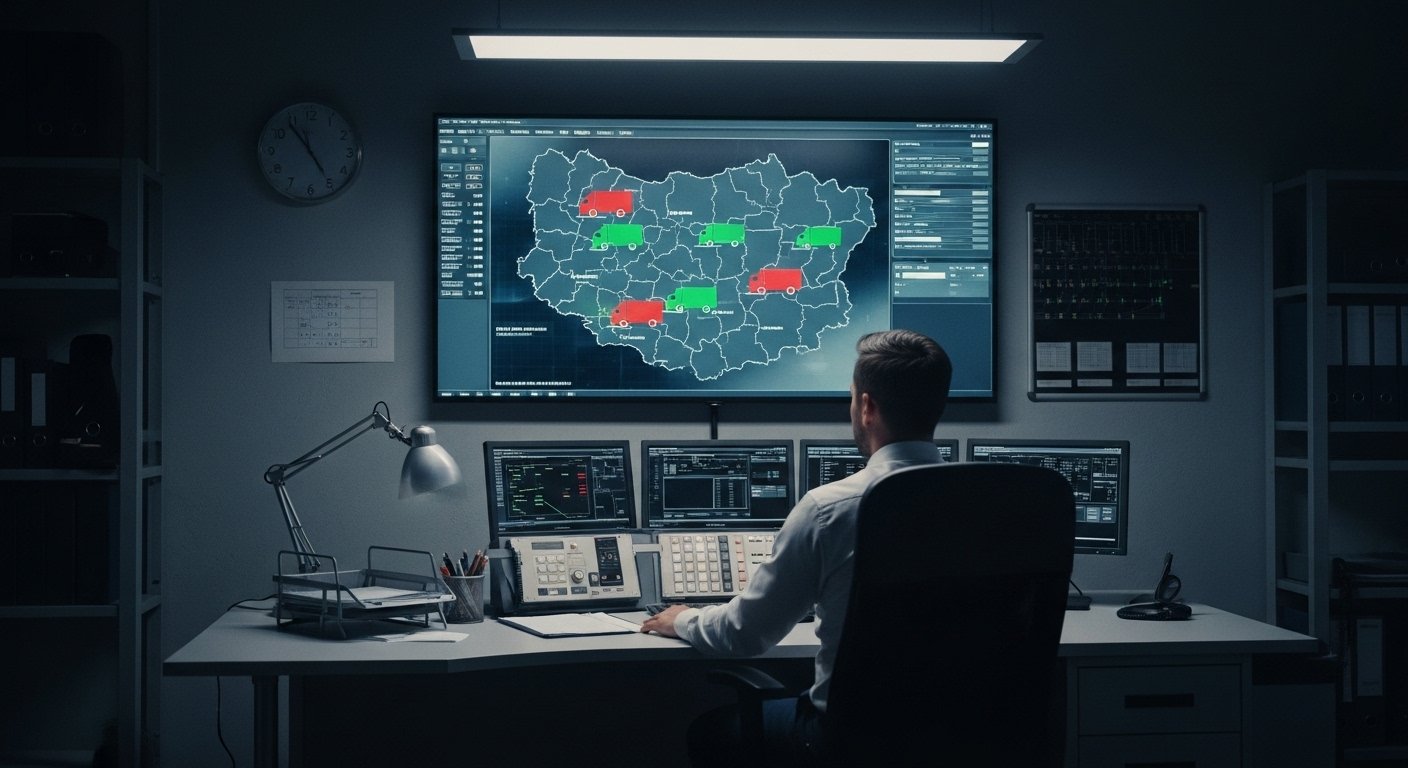
Além de fornecer informações precisas para o local, Os sistemas GPS aumentam o planejamento do caminho, avaliando informações de tráfego em tempo real e recomendando cursos ideais. Essa capacidade é especialmente benéfica para a gestão da frota de carros nos negócios de GPS, onde eficácia e confiabilidade são essenciais. Aproveitando o sistema GPS Surack365, Os supervisores de frota podem monitorar os locais dos veículos, otimizar rotas, e verifique se os veículos autônomos funcionam de maneira eficiente e segura, Ajudando ainda mais no desempenho do sistema de roubo de soluções.
Eventualmente, A integração suave do GPS com várias outras tecnologias sensoriais permite que os veículos autônomos realizem uma extensa compreensão de seu ambiente. Essa abordagem alternativa não apenas melhora a navegação e a colocação de precisão, mas também garante que esses veículos possam funcionar de maneira confiável em problemas de direção variados. À medida que a tecnologia GPS passa a desenvolver, Seu papel na direção autônomo certamente se expandirá, Liderando o caminho para sistemas de auto-governança avançada e eficiente e sistemas de proteção de veículos aprimorados.
Desafios e restrições de GPs na direção autônoma
A integração de sistemas GPS, como o sistema GPS Surack365, em tecnologia de direção autônoma oferece uma série de desafios e restrições que precisam ser cuidadosamente tratados. Um desafio considerável é indicar bloqueios e perturbações. Atmosferas metropolitanas, Freqüentemente chamado de ‘Urban Canyons,’ posicionar um desafio considerável devido a grandes estruturas que podem refletir ou obstruir o GPS indica. De forma similar, passagens e locais muito florestais apresentam situações onde os GPs indicam que são completamente derramados, desencadeando a navegação de imprecisões. Tais suscetibilidades enfatizam a necessidade de sistemas de imobilizadores de alarme de carro duráveis.
O tempo também pode afetar a precisão dos sistemas de GPS. Fatores como chuvas pesadas, neve, ou nevoeiro espesso pode deteriorar -se indicar qualidade, proeminente a possíveis inconsistências na colocação de informações. Essa variabilidade requer a necessidade de soluções aprimoradas para garantir procedimentos confiáveis, independentemente de problemas meteorológicos. Além disso, Os GPs indicam falsificação e interferência continuam sendo preocupações críticas. A falsificação envolve a transmissão prejudicial de GPS incorreto indica, que pode enganar o sistema de navegação de um veículo autônomo. Jamming, Por outro lado, envolve a transmissão de indica que bloqueia regularidades legítimas de GPS, desencadear uma perda de indicar integridade, Produção eficaz de soluções de soluções projetos muito mais críticos.
Para reduzir essas suscetibilidades, A redundância nos sistemas de navegação é crucial. Tecnologias correspondentes, como sistemas de navegação inercial (Ins) e a odometria estética está sendo incorporada progressivamente para apoiar as informações do GPS. Ins, que depende de unidades de detecção de movimento para rastrear as mudanças de posição, Fornece informações contínuas de navegação ao longo de interrupções temporárias de GPS. A odometria estética usa informações de came de vídeo para estimar o movimento do veículo sobre seus ambientes, reforçando ainda mais a confiabilidade do sistema de navegação e sistemas de proteção de veículos.
Pesquisas e desenvolvimentos em andamento estão concentrados em melhorar a confiabilidade e a precisão dos sistemas GPS para veículos autônomos. As iniciativas consistem no desenvolvimento de receptores de multi-frequência e multi-conslação, que o uso indica de vários sistemas de satélite para melhorar a precisão e a durabilidade. Além disso, As fórmulas de inteligência artificial estão sendo utilizadas para antecipar e corrigir erros potenciais em tempo real. Esses desenvolvimentos têm como objetivo produzir uma estrutura de navegação durável, garantindo que os sistemas GPS, como o rastreador GPS Protrack, pode efetivamente apoiar as demandas de direção autônoma e gerenciamento de frotas de carros em um ambiente de negócios GPS, e forneça recursos de imobilizador avançado do sistema de alarme de carro.
O futuro do GPS e a direção autônoma
O futuro da tecnologia GPS no mundo da direção autônoma tem uma promessa enorme, de propriedade de desenvolvimentos contínuos e desenvolvimentos técnicos. Entre um dos desenvolvimentos mais consideráveis no horizonte está os satélites GPS da próxima geração. Esses satélites avançados são projetados para fornecer maior precisão, melhorado indica resistência, e maior durabilidade versus perturbação e tiro. Esse desenvolvimento é crucial para a navegação precisa exigida por veículos autônomos, Juntamente com tecnologias de imobilizador de alarme de carro avançado.
Desenvolvimentos no cinemático em tempo real (RTC) A colocação também está preparada para transformar a paisagem GPS. A tecnologia RTK melhora a precisão do GPS padrão, utilizando indica adicionais nos terminais básicos, diminuindo assim os centímetros simples. Esse grau de precisão é essencial para o procedimento seguro e eficiente de carros autônomos, especialmente em atmosferas metropolitanas, onde a colocação precisa da pista e a descoberta de desafios são críticas, e aprimora muito os sistemas de proteção de veículos.
A integração do GPS com vários outros sistemas globais de navegação por satélite (GNSS) como Glonass, Galileu, E Beidou é mais um padrão formando o futuro. Combinando informações de várias constelações do GNSS, Veículos autônomos podem realizar também maior precisão e confiabilidade na colocação. Este Multi-GNSS se aproxima que mitiga os perigos associados a bloqueios indicados ou interrupções atmosféricas, Garantir habilidades contínuas de navegação e reforçar a segurança do sistema de roubo de soluções eficazes.
Olhando com antecedência, As melhorias contínuas na tecnologia GPS têm maior probabilidade de ter amplos impactos no desenvolvimento e implementação de veículos autônomos. A precisão e a confiabilidade aprimoradas do GPS suportarão fórmulas de direção autônomo mais avançadas, permitindo que os veículos procurem atmosferas complexas com maior facilidade. Além disso, Esses desenvolvimentos podem levar os órgãos reguladores a atualizar requisitos e padrões para garantir a integração segura de veículos autônomos nas instalações de transporte atuais.
Passando pelos aspectos tecnológicos, As ramificações mais amplas desses desenvolvimentos para a indústria e cultura de transporte são consideráveis. Sistemas GPS mais precisos e confiáveis facilitarão a extensa promoção de veículos autônomos, proeminente a potenciais reduções no engarrafamento, acidentes, e emissões. Além disso, A eficácia adquira no gerenciamento de frotas de carros e aplicativos de negócios de GPS podem mudar a logística e o transporte de massa, eventualmente adicionando a uma comunidade de movimentos metropolitanos mais inteligentes e duradouros, enquanto integra sistemas avançados de proteção de veículos.