Problemas de navegación de Galileo Advertencia de deterioro del sistema
El sistema de navegación de Galileo no puede actualizar el satélite Ephemeris normalmente. El llamado Ephemeris son los datos importantes para determinar la posición de espacio-tiempo de la nave espacial, lo que significa que los usuarios de todo el mundo pronto no podrán recibir la señal correcta del sistema. La advertencia de deterioro del sistema también revela una información importante, Esa es la causa de la falla es desconocida, y es imposible predecir cuándo se restaurará el servicio.
En julio 25 el año pasado, Un cohete portador de empuje grande-5 de Ariane-5 envió con éxito cuatro satélites en red numerados FOC FM-19, 20, 21, y 22 en la órbita programada, lo que significa que el sistema Galileo ha sido minuciosamente operado para 15 años. Básicamente tiene las capacidades de hardware de la navegación global. Según el plan, El sistema proporcionará servicios de posicionamiento de 10 metros a usuarios de todo el mundo este año, Pero se quedó corto cuando estaba a punto de hacerse. No es una exageración usar el término “malas noticias”.
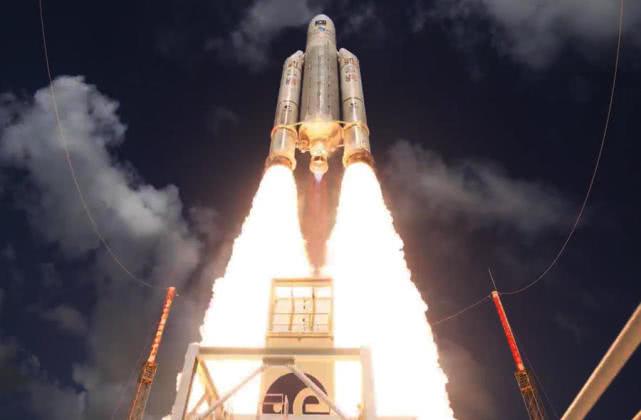

Ariane-5 Rocket lanza el satélite de redes Galileo
El sistema global de navegación por satélite es un apoyo estratégico importante para el estado de un país importante. A menudo enfatizamos su valor económico. Sin embargo, Como todos sabemos, El uso militar es su primer valor, y el sistema de navegación de Galileo no es una excepción.
El sistema de navegación de Galileo también se considera un símbolo de la unidad de la Unión Europea. El sistema fue iniciado por primera vez por Alemania, Francia, e Italia. La razón fundamental para la creación de un sistema de navegación global autónomo y controlable es la desconfianza de Europa del sistema GPS, Porque este último inyecta un “mecanismo de disponibilidad selectiva” mientras proporciona servicios de navegación al mundo, lo que significa que las señales GPS se limitan artificialmente a la precisión de la navegación. Los europeos se preocupan de que los GP también los ataquen si encuentran situaciones extremas.