Introduction à la technologie GPS d'entreprise
Système de positionnement global (GPS) la technologie a connu une évolution remarquable depuis sa création, passer d’aides à la navigation rudimentaires à des systèmes sophistiqués désormais indispensables dans diverses opérations commerciales. Initialement développé à des fins militaires dans les années 1970, La technologie GPS a rapidement trouvé sa place dans les applications civiles, ouvrant la voie à son intégration dans les processus métiers. Au fil des décennies, la dépendance au GPS s'est développée de façon exponentielle, notamment en logistique, gestion de flotte de véhicules, et optimisation de la supply chain.
Les premiers stades de la technologie GPS étaient caractérisés par des outils de navigation de base permettant un suivi de localisation simple.. Cependant, à mesure que les progrès technologiques progressaient, les capacités des systèmes GPS aussi. L'introduction des unités GPS commerciales dans les années 1980 a marqué une étape importante, offrir aux entreprises la possibilité d’améliorer leur efficacité opérationnelle et leurs processus décisionnels. À la fin des années 1990 et au début des années 2000, La technologie GPS était devenue plus accessible, conduisant à son adoption généralisée dans diverses industries.
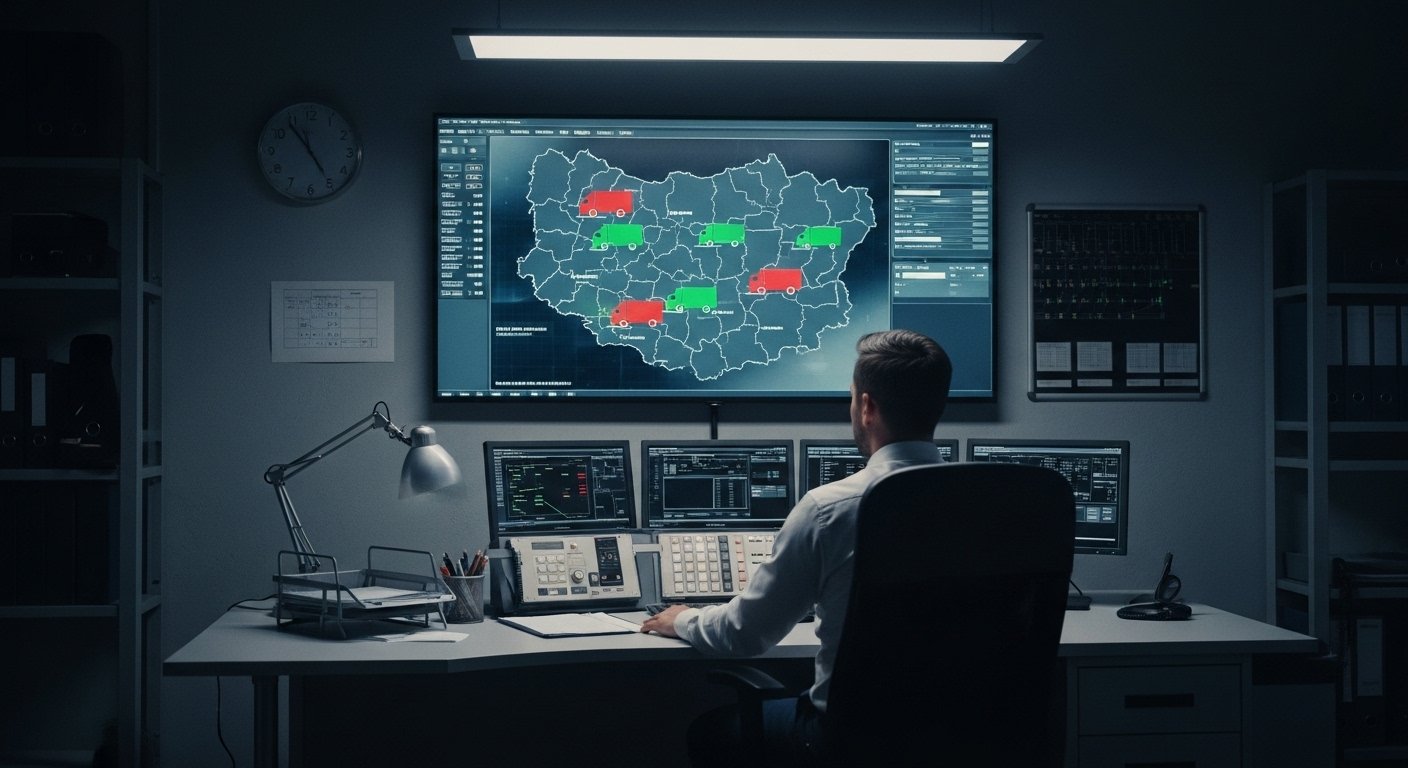
Dans les applications métiers modernes, La technologie GPS fait partie intégrante de la gestion de flotte de véhicules. Traceurs GPS avancés, comme le tracker GPS Protrack, permettre aux entreprises de surveiller et de gérer leurs flottes avec une précision sans précédent. La plateforme de suivi Protrack, par exemple, fournit des données en temps réel sur l'emplacement des véhicules, itinéraires, et indicateurs de performances, optimisant ainsi les opérations de la flotte et réduisant les coûts opérationnels. Ce niveau de suivi et d'analyse détaillé était inimaginable il y a quelques décennies à peine..
Les étapes clés de l'évolution de la technologie GPS d'entreprise incluent l'avènement des systèmes d'augmentation par satellite (SBAS), qui améliorent la précision et la fiabilité des signaux GPS. En plus, L'intégration du GPS avec d'autres technologies comme les systèmes d'information géographique (Gis) Et l'Internet des objets (IdO) a révolutionné le fonctionnement des entreprises. Ces progrès ont conduit à des solutions de pointe qui non seulement suivent mais prédisent et optimisent également divers aspects de la logistique commerciale et des chaînes d'approvisionnement.
Aujourd'hui, La technologie GPS est à l'avant-garde de l'innovation, évoluant continuellement pour répondre aux besoins dynamiques des entreprises modernes. Avec le développement continu de systèmes GPS plus puissants et polyvalents, Les entreprises sont mieux équipées pour naviguer dans les complexités des chaînes d'approvisionnement mondiales et maintenir un avantage concurrentiel dans leurs industries respectives.
Tendances et innovations émergentes
Le paysage de la technologie GPS subit une transformation significative, tiré par les tendances et les innovations émergentes qui remodèlent sur le fonctionnement des entreprises. L'une des progrès les plus notables est le suivi en temps réel. Cette technologie permet aux entreprises de surveiller les actifs et le personnel avec une précision et une immédiateté sans précédent. Le suivi en temps réel améliore non seulement l'efficacité opérationnelle, mais améliore également la sécurité et la conformité dans les secteurs tels que la logistique et le transport.
Le géofencing est une autre caractéristique innovante qui gagne du terrain. En créant des limites virtuelles, Les entreprises peuvent recevoir des alertes lorsqu'un actif entre ou quitte une zone spécifiée. Cette capacité est particulièrement bénéfique pour la gestion de la flotte de véhicules, car il aide à l'optimisation des itinéraires et à la prévention de l'utilisation non autorisée. Les entreprises utilisant le géofencing peuvent réduire considérablement les coûts opérationnels et améliorer les protocoles de sécurité.
L'intégration de la technologie GPS avec l'Internet des objets (IdO) et l'intelligence artificielle (IA) ouvre de nouveaux horizons. Les appareils IoT peuvent collecter de grandes quantités de données, quelles algorithmes d'IA analysent pour fournir des informations exploitables. Par exemple, Dans le contexte de la gestion de la flotte de véhicules, Les capteurs IoT peuvent surveiller les conditions des véhicules en temps réel, Alors que l'IA peut prédire les besoins de maintenance, Empêchant ainsi les temps d'arrêt coûteux. Cette intégration transparente améliore la précision et l'efficacité des opérations commerciales, conduisant à la prise de décision éclairée.
Plusieurs entreprises sont à l'avant-garde de ces innovations. Protrack, Par exemple, Offre une plate-forme de suivi complète qui exploite le suivi en temps réel, géolocalisation, et l'intégration IoT pour fournir aux entreprises des informations détaillées sur leurs opérations. La plate-forme de suivi des protracks se distingue par son interface conviviale et ses capacités analytiques robustes, En faire un outil précieux pour les entreprises visant à optimiser leur gestion de la flotte.
Alors que ces technologies continuent d’évoluer, Ils sont prêts à révolutionner divers secteurs commerciaux. L'intégration du GPS avec les technologies émergentes améliore non seulement la précision et l'efficacité, mais permet également aux entreprises de prendre des décisions basées sur les données, augmentant ainsi la productivité et la rentabilité globales.
Impact sur les opérations commerciales
Les développements futuristes dans la technologie GPS sont sur le point de révolutionner les opérations commerciales dans diverses industries. En logistique, Des solutions GPS avancées comme la plate-forme de suivi de Protrack permettent aux entreprises de surveiller leurs flottes en temps réel, Optimisation des voies et réduction de la consommation de carburant. Cela conduit à des économies de coûts importantes et améliore l'efficacité opérationnelle, fournir un avantage concurrentiel.
Dans la gestion des actifs, L'intégration de trackers GPS sophistiqués assure le suivi précis des actifs précieux. Les entreprises peuvent empêcher le vol, réduire les pertes, et maintenir des enregistrements d'inventaire précis. Par exemple, Une entreprise de fabrication utilisant des trackers GPS peut immédiatement localiser l'équipement mal placé, minimisant ainsi les temps d'arrêt et stimuler la productivité.
La productivité des employés est un autre domaine où la technologie GPS a un impact substantiel. En utilisant des trackers GPS, Les entreprises peuvent surveiller l'emplacement et le mouvement de leur personnel de terrain, s'assurer qu'ils adhèrent à leurs horaires et leurs itinéraires. Cela améliore non seulement la responsabilité, mais aide également à déployer des ressources plus efficacement. Un exemple est une chaîne de vente au détail qui utilise les données GPS pour confirmer que le personnel de livraison suit les itinéraires les plus efficaces, assurant ainsi des livraisons en temps opportun et améliorant la satisfaction des clients.
La satisfaction du client est directement influencée par la fiabilité et l'efficacité des services fournis. Avec des capacités GPS améliorées, Les entreprises peuvent offrir des fenêtres de livraison précises, suivi en temps réel, et les mises à jour immédiates des clients. Cette transparence renforce la confiance et la loyauté. Une entreprise de transport, par exemple, peut tirer parti de la technologie GPS pour fournir des mises à jour ETA précises aux clients, Assurer une expérience de service transparente.
Des études de cas illustrent ces avantages vivement. Considérez une entreprise de logistique qui a implémenté le tracker GPS ProTrack sur toute sa flotte. Le résultat a été un 20% réduction des coûts de carburant et un 15% Augmentation des livraisons à temps au cours de la première année. De la même manière, Une entreprise de fabrication qui a adopté la gestion des actifs GPS a rapporté un 30% réduction de la perte d'équipement et d'un 25% Amélioration de l'efficacité opérationnelle.
En résumé, L'intégration de la technologie GPS avancée dans les opérations commerciales peut entraîner une amélioration profonde de la logistique, gestion des actifs, productivité des employés, et la satisfaction du client. Ces progrès promettent non seulement des économies de coûts et une efficacité accrue, mais aussi un avantage concurrentiel important dans l'environnement commercial au rythme rapide d'aujourd'hui.
Défis et perspectives futures
Mise en œuvre des technologies GPS de nouvelle génération en affaires, comme la plate-forme de suivi des protracks, présente plusieurs défis qui doivent être relevés pour une adoption réussie. L'une des préoccupations les plus importantes est la confidentialité des données. À mesure que les entreprises collectent et traitent de grandes quantités de données de localisation via des trackers GPS, S'assurer que ces informations sensibles sont protégées et utilisées éthiquement est primordiale. Les entreprises doivent se conformer à divers réglementations sur la protection des données, comme le RGPD, pour protéger leurs clients’ et les employés’ confidentialité.
La cybersécurité est un autre problème critique. Les systèmes GPS avancés peuvent être vulnérables aux cyberattaques, qui peut compromettre l'intégrité des opérations de gestion des flottes de véhicules. Les entreprises doivent investir dans des mesures de cybersécurité robustes pour protéger leurs systèmes de suivi GPS contre les menaces potentielles. Cela comprend des mises à jour logicielles régulières, cryptage des transmissions de données, et formation des employés sur les meilleures pratiques de cybersécurité.
Les coûts associés à la mise à niveau des systèmes existants pour intégrer la technologie GPS de nouvelle génération peuvent également être prohibitifs pour certaines entreprises. Investissement dans un nouveau matériel, comme les trackers GPS avancés, Et l'intégration de plateformes de suivi sophistiquées peut nécessiter des ressources financières substantielles. Cependant, les avantages à long terme, comme l'amélioration de l'efficacité de la flotte et réduit les coûts opérationnels, justifient souvent les dépenses initiales.
Les considérations réglementaires et éthiques jouent également un rôle crucial dans la mise en œuvre des technologies GPS avancées. Les entreprises doivent naviguer dans un paysage complexe de réglementations qui régissent l'utilisation des dispositifs de suivi GPS et les données qu'elles génèrent. Considérations éthiques, comme le potentiel de surveillance et de surveillance des employés, Doit également être soigneusement géré pour maintenir la confiance et la transparence au sein de l'organisation.
Regarder vers l'avenir, L'avenir de la technologie GPS d'entreprise détient un immense potentiel. Des innovations telles que le suivi en temps réel, analyse prédictive, et l'intégration avec d'autres dispositifs IoT devrait révolutionner la gestion de la flotte de véhicules. Il est essentiel de rester en avance sur ces tendances technologiques pour que les entreprises restent compétitives et tirent parti de tous les avantages des solutions GPS modernes.
En conclusion, Bien que les défis existent, Les progrès de la technologie GPS, illustré par des plateformes comme Protrack, Offrez des opportunités importantes pour les entreprises. En abordant la confidentialité des données, cybersécurité, et des problèmes de réglementation, et investir dans les dernières technologies, Les entreprises peuvent améliorer leur efficacité opérationnelle et garantir un avantage concurrentiel sur le marché.